UPDATES
IBS Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials
Total : 62, Now : 4 page

A tech jewel: Converting graphene into diamond film
- Synthesis of the thinnest possible diamond-like material starting from bilayer graphene and without high pressure -
Can two layers of the “king of the wonder materials,” i.e. graphene, be linked and converted to the thinnest diamond-like material, the “king of the crystals”? Researchers of the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM) within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea) have reported in Nature Nanotechnology the first experimental observation of a chemically induced conversion of large-area bilayer graphene to the thinnest possible diamond-like material, under moderate pressure and temperature conditions. This flexible, strong material is a wide-band gap semiconductor, and thus has potential for industrial applications in nano-optics, nanoelectronics, and can serve as a promising platform for micro- and nano-electromechanical systems.
Diamond, pencil lead, and graphene are made by the same bu…
작성자 : CMCM
2019.12.11

IBS 과학자 7인, 세계에서 가장 영향력 있는 연구자로 선정
클래리베이트 애널리틱스 발표…역대 국내 HCR 중 13%가 IBS 소속
IBS 전경사진
▲ 클래리베이트 애널리틱스가 선정한 2019 HCR에는 IBS 소속 연구자 7명이 이름을 올렸다.
지금까지 HCR로 선정된 IBS 연구자는 총 11명이다.
올 한해 세계에서 가장 영향력 있는 연구를 펼친 연구자 명단에 기초과학연구원(IBS) 소속 7명의 연구자가 이름을 올렸다.
글로벌 학술정보서비스 분석기업 클래리베이트 애널리틱스가 20일 발표한 ‘2019 세계에서 가장 영향력 있는 연구자(Highly Cited Researcher·HCR)’에 따르면 2019년 국내 HCR 41명(중복수상 포함 45명) 중 IBS 소속 연구자는 7명(중복수상 포함 9명)으로 확인됐다. 국내 소속기관 중에서는 서울대(9명)에 이어 두 번째로 많은 HCR 연구자를 배출했다.
클래리베이트는 매년 각 분야에서 해당 연도에 가장 많이 인용된 상위 1% 논문(Highly Cited Papers)을 작성한 연구자를 HCR로 선정하고 있다. HCR은 논문의 피인용 횟수를 근거로 선정되기 때문에 세계 각지의 동료 연구자들에게 인정을 받은 연구자라는 의미가 있다. 6년째를 맞은 올해는 22개 분야에서 60여 개국 총 6,216명의 연구자가 HCR로 선정됐다.
로드니 루오프 단장(다차원 탄소재료 연구단)과 현택환 단장(나노입자 연구단)은 화학/재료과학의 2개 분야에 중복 선정되며 올해로 6년 연속 HCR 명단에 이름을 올렸다. 한편, 장석복 단장(분자활성 촉매반응 연구단)은 화학 분야에서 5년 연속 선정됐다.
이와 함께 생물학 및 생화학 분야에서는 김진수 단장(유전체 교정 연구단), 크로스필드 분야에서는 이영희 단장(나노구조물리 연구단)과 악셀 팀머만 단장(기후물리 연구단), 재료과학 분야에서 김대형 부연구단장(나노입자 연구단)이 작년에 이어 올해도 HCR로 선정됐다.
지금까지 총 11명의…
작성자 : CMCM
2019.11.26
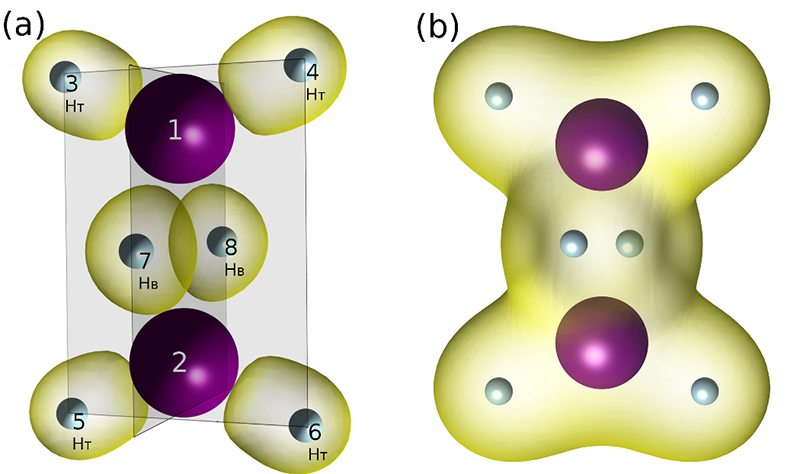
CMCM Research Update Charge transfer, the secret weapon of liquid gallium
-Understanding the interactions between Gallium and Hydrogen-
The Materials group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials directed by UNIST Distinguished Professor Rodney S. Ruoff, within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), have discovered a large transfer of charge from metal atoms to both hydrogen molecule and hydrogen atoms – a result with potential significance in utilizing hydrogen as clean energy source, as well as in chemical synthesis. These findings were based on their observations from computer simulations of a hydrogen – liquid gallium system held at 100 °C.
Metals are materials that can conduct electricity and heat. They are commonly thought of as shiny solids, but can also exist as liquids. A well-known example of a liquid metal is mercury. Liquid metals find a wide variety of potential uses. For example, there are a growing number of studies of their use as reaction solvents…
작성자 : CMCM
2019.11.19
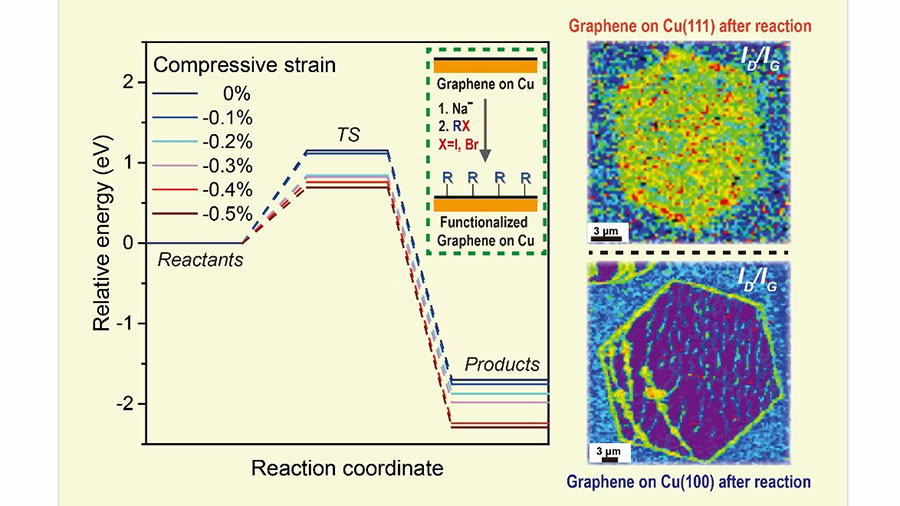
Compressive Stress in Single Crystal Graphene Drives Chemistry on the Graphene Surface
Researchers synthesize a new 2D Metal Organic Framework with an ever-growing list of possible applications
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) growth of graphene on metal substrates, especially on copper (Cu) foils, is an effective and popular technique to synthesize graphene approaching perfect crystallinity. Covalent chemical functionalization of defect-free (and thus the most chemically inert) graphene on Cu with deliberately chosen appending groups is not only fundamentally important for understanding its chemistry, but also for tailoring its structures and properties, and could be beneficial in practical uses such as for electrochemical sensors, optical devices, non-corroding current collectors, and as electrodes in electrical energy storage systems, among other reasons. The chemical reactivity of graphene on Cu foil substrates is a currently a topic of fundamental scientific study.
▲ Fi…
작성자 : CMCM
2019.11.08
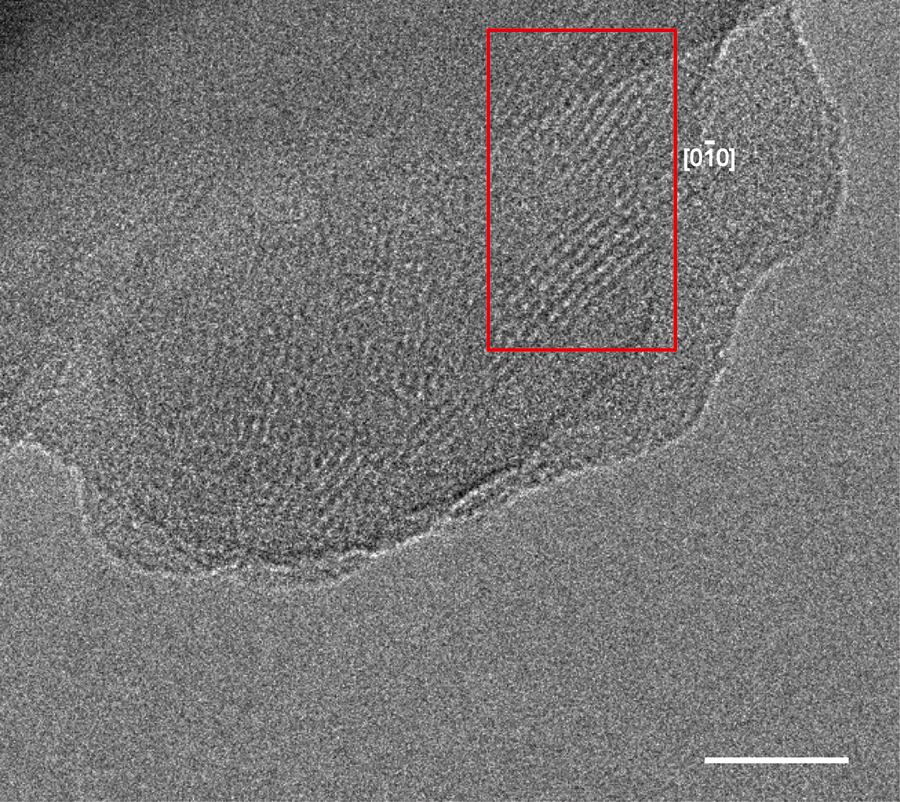
Novel sponge-like 2D material with interesting electrical conductivity and magnetic properties
Researchers synthesize a new 2D Metal Organic Framework with an ever-growing list of possible applications
Chemists at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea), have reported the synthesis of a novel type of 2D metal organic framework (MOF) with interesting electrical conductivity and magnetic properties. Published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, this new material may potentially contribute to optoelectronics, photovoltaics, (photo)electrocatalysis, and energy storage.
Also known as sponge-like or Swiss-cheese-like materials, MOFs are made of metal ions connected to organic ligands and are characterized by nano-sized holes. IBS researchers in collaboration with the School of Materials Science at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) designed and synthesized Ni(II) tet…
작성자 : CMCM
2019.10.31
베베 꼬인 2차원 이중나선모양의 신소재 개발
약점을 기회로 활용…지금껏 보고된 적 없는 새로운 구조 탄생
▲ 연구가 게재된 ‘나노 레터스’ 7월호 표지
사과 맛과 딸기 맛을 모두 즐길 수 있는 유명 아이스크림처럼, 베베 꼬인 형태의 새로운 소재가 개발됐다.
이종훈 기초과학연구원(IBS) 다차원 탄소재료 연구단 그룹리더(UNIST 신소재공학부 교수) 팀은 2차원 육방정계 질화붕소(h-BN, hexagonal Boron Nitride)를 이중나선 구조로 성장시키는 데 성공했다.
육방정계 질화붕소는 그래핀과 유사한 육각형 구조를 가지면서도 하얀색을 띄어 ‘화이트 그래핀’으로도 불린다. 전기가 통하지 않는 대표적인 2차원 부도체 물질이다. 열에 강하고, 방사능도 막을 수 있어 전자기기는 물론 비행기, 우주선과 같은 가볍고 열‧화학적 안정성이 요구되는 분야에 두루 활용될 것으로 기대되고 있다.
연구진은 단결정 육방정계 질화붕소를 성장시키던 중 우연히 두개의 결정이 서로 꼬이며 성장하는 ‘이중나선 육방정계 질화붕소’를 발견했다. 격자구조가 서로 반대인 두 개의 결정이 맞닿은 역위상 경계(Antiphase Boundary)에서 두 결정이 서로를 휘감으며 지금껏 보고된 적 없는 새로운 구조로 성장함을 발견한 것이다.
연구의 제1저자인 박효주 IBS 다차원 탄소재료 연구단 연구위원은 “지금까지 2차원 재료 성장 과정에서 역위상 경계는 결함으로 여겨졌다”며 “결함을 역으로 활용해 새로운 구조 및 물성을 가진 신소재를 개발한 것”이라고 설명했다.
▲ 이중나선 육방정계 질화붕소(h-BN)의 성장 메커니즘 모식도. 역위상 경계를 중심으로 두 개의 결정이 뒤엉키며 이중나선 구조를 형성한다.
이후 연구진은 투과전자현미경(TEM)을 이용한 관찰 및 컴퓨터 시뮬레이션을 통해 이중나선구조의 형성 메커니즘을 원자 수준에서 분석했다. 그 결과, 역위상 경계에서 발생하는 두 개의 나사 전위(Screw Dislocation) 쌍이 뒤얽힌 이…
작성자 : CMCM
2019.10.14
