UPDATES
Researchers synthesize a new 2D Metal Organic Framework with an ever-growing list of possible applications
Chemists at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea), have reported the synthesis of a novel type of 2D metal organic framework (MOF) with interesting electrical conductivity and magnetic properties. Published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, this new material may potentially contribute to optoelectronics, photovoltaics, (photo)electrocatalysis, and energy storage.
Also known as sponge-like or Swiss-cheese-like materials, MOFs are made of metal ions connected to organic ligands and are characterized by nano-sized holes. IBS researchers in collaboration with the School of Materials Science at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) designed and synthesized Ni(II) tetraaza[14]annulene-linked MOF (NiTAA-MOF), where the metal component is nickel and the nickel tetraaza[14]annulene molecules are used as MOF building blocks for the first time.
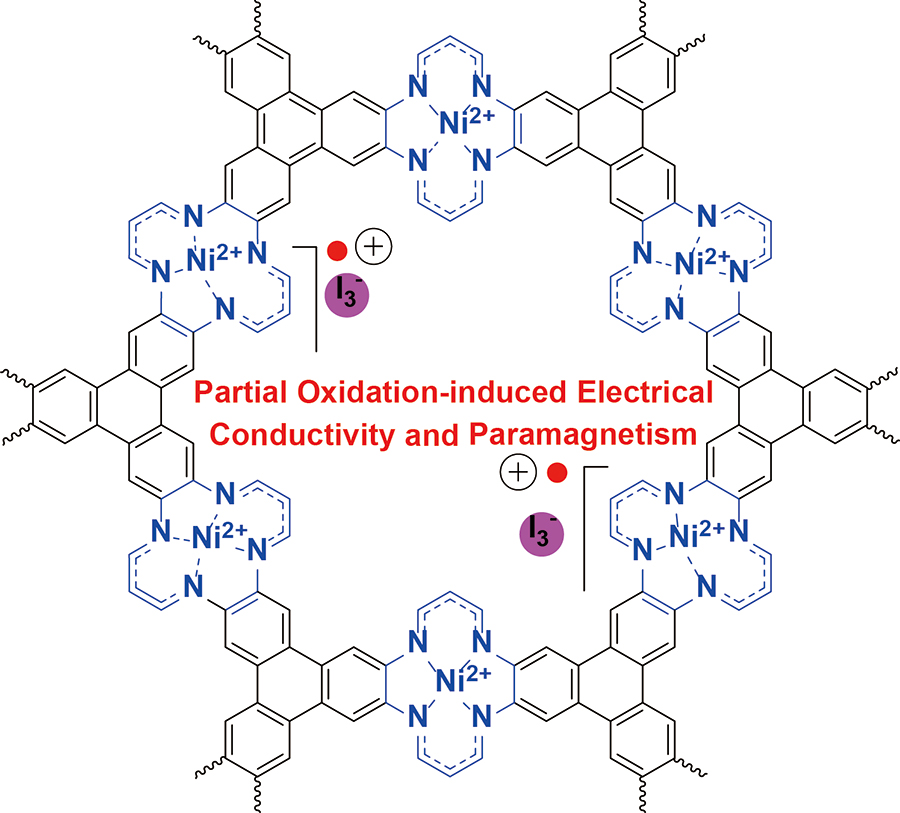
▲ Figure 1. Chemical structure of iodine-doped Ni(II) tetraaza[14]annulene-linked MOF (NiTAA-MOF). While NiTAA-MOF is an insulator, the oxidized molecule acquires electrical conductivity and paramagnetism.
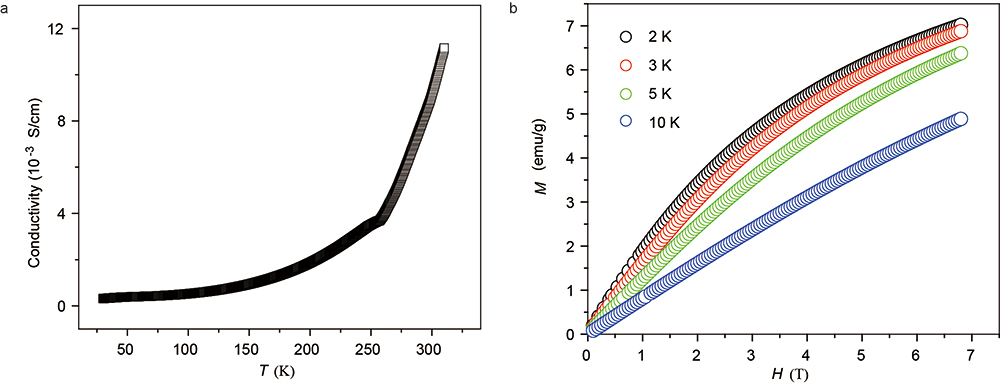
▲ Figure 2. Electrical conductivity and magnetic properties of iodine-doped NiTAA-MOF. a) Electrical conductivity as a function of temperature. b) Magnetization increases with decreasing temperature, a typical feature of paramagnetic materials.
The researchers discovered that doping this MOF with iodine changes its conductivity and magnetism. Pristine NiTAA-MOF conducts poorly. It is actually an insulator with an electrical conductivity smaller than 10-10 Siemens per centimeter. However, when it is chemically oxidized by iodine, the same measurement rises to 0.01 Siemens per centimeter (the larger this number, the better the conductor). This result shows the vital role of ligand oxidation in the electrical conductivity of some 2D MOFs, expanding the understanding of the origin of electrical conductivity in this type of MOFs.
In addition, the team checked how this material becomes magnetized in an applied magnetic field. Magnetization measurements performed by the researchers of the School of Materials Science showed that iodine-doped NiTAA-MOF is paramagnetic, that is it is weakly attracted by an external magnetic field, and becomes antiferromagnetic at very low temperatures. This means that it could become useful as a polarizing agent in dynamic nuclear polarization-nuclear magnetic resonance (DNP-NMR) that is used in experiments for material characterization.
The 2D MOF structure was also modeled through detailed calculations and analyzed by a variety of methods, such as X-ray diffraction, infrared, X-ray photoelectron, diffuse reflectance UV-vis, electron paramagnetic resonance, and Raman spectroscopies.
“Our work can contribute to the fundamental understanding of structure-property relationships in 2D electrically conductive MOFs, and may pave the way to develop new electrically conductive MOFs,” says Professor Ruoff, one of the corresponding authors of this study and UNIST professor. “Besides, the as-synthesized and iodine-doped NiTAA-MOF might be applicable in catalase mimics, catalysis, and energy storage.”
- IBS 연구진, 금속유기구조체(MOF)의 전도성 향상 메커니즘 규명 -
대용량 에너지 저장장치의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있는 신소재가 나왔다. 기초과학연구원(IBS, 원장 대행 김영덕) 다차원 탄소재료 연구단(단장 로드니 루오프) 연구진은 울산과학기술원(UNIST)과의 공동연구를 통해 슈퍼커패시터용 전극물질로 각광받는 금속유기구조체1)(MOF)의 전기적 특성을 향상시킬 수 있는 메커니즘을 규명하고, 자성과 전도성을 동시에 지닌 새로운 소재(NiTAA-MOF)를 개발했다.
전자기기의 성능 향상과 함께 높은 출력을 낼 수 있는 에너지 저장장치에 대한 요구가 커지고 있다. MOF는 슈퍼커패시터, 2차 전지 등 대용량 에너지 저장장치의 전극 소재로 주목받는다. MOF는 금속과 탄소 물질(유기물)이 결합해 이룬 다공성 소재다. 이를 전극으로 사용할 경우 넓은 표면적에서 산화-환원 반응을 활발히 일어나기 때문에 높은 에너지 저장능력 및 성능을 갖는 에너지 소자를 만들기 유리하다.
MOF 기반 에너지 소자의 상용화를 위해서는 MOF의 전기적 성질에 대한 근본적인 이해가 필요하다. 하지만 MOF의 어떤 구조적·화학적 변화가 전기 전도성에 영향을 미치는지에 대해서는 아직까지 명확히 밝혀진 바 없다.
MOF의 전기전도성을 높일‘히든카드’를 찾아내기 위해 연구진은 우선 거대한 고리 형태의 새로운 금속유기구조체를 설계했다. 니켈(Ⅱ)테트라[14]아자아눌렌-금속유기구조체(NiTAA-MOF)는 니켈 원자 주변에 4개의 질소 원자가 결합한 MN4(M=금속, N=질소) 유형의 기본 구조를 갖는다. NiTAA는 전기전도성을 가진 물질로 촉매, 트랜지스터, 염료감응태양전지 등에 사용되지만, 금속유기구조체의 연결체로 사용된 적은 없다.
연구진이 설계한 덩어리(벌크) 형태의 NiTAA-MOF는 기본적으로 전기가 통하지 않는(절연) 상태이다. 하지만 요오드 증기를 이용해 80도의 온도에서 열처리를 진행하며 NiTAA-MOF를 화학적으로 산화시키면 300K(26.85℃)의 온도에서 0.01S/㎠(지멘스 퍼 제곱센티미터)의 전기전도도를 나타낸다. 이는 별도의 전도체를 첨가할 필요 없이 전극으로 사용하기에 충분히 높은 전기전도도다.
유정우 UNIST 신소재공학부 교수는“리간드 산화2)에 의해서 부도체였던 2차원 금속유기구조체에 전기 전도성이 유도된다는 것을 보여준 것”이라며 “더 나아가 리간드 산화에 따라 MOF의 스핀 농도를 증가시켜 자성을 구현할 수 있음도 확인했다”고 설명했다.
로드니 루오프 단장은“2차원 금속유기구조체의 구조와 전기적 특성 간의 관계에 대한 근본적인 이해를 제시한 것으로, 새로운 전기전도성 금속유기구조체를 개발할 수 있는 길을 제시했다”며 “합성된 NiTAA-MOF는 에너지 소자뿐만 아니라 촉매, 센서 등 다양한 광전자공학 분야에서 응용할 수 있을 것”이라고 말했다.
연구결과는 화학분야 세계적 권위지인 ‘미국화학회지(Journal of the American Chemical Society·JACS, IF 14.695)’10월 14일자 온라인 속보로 실렸다.
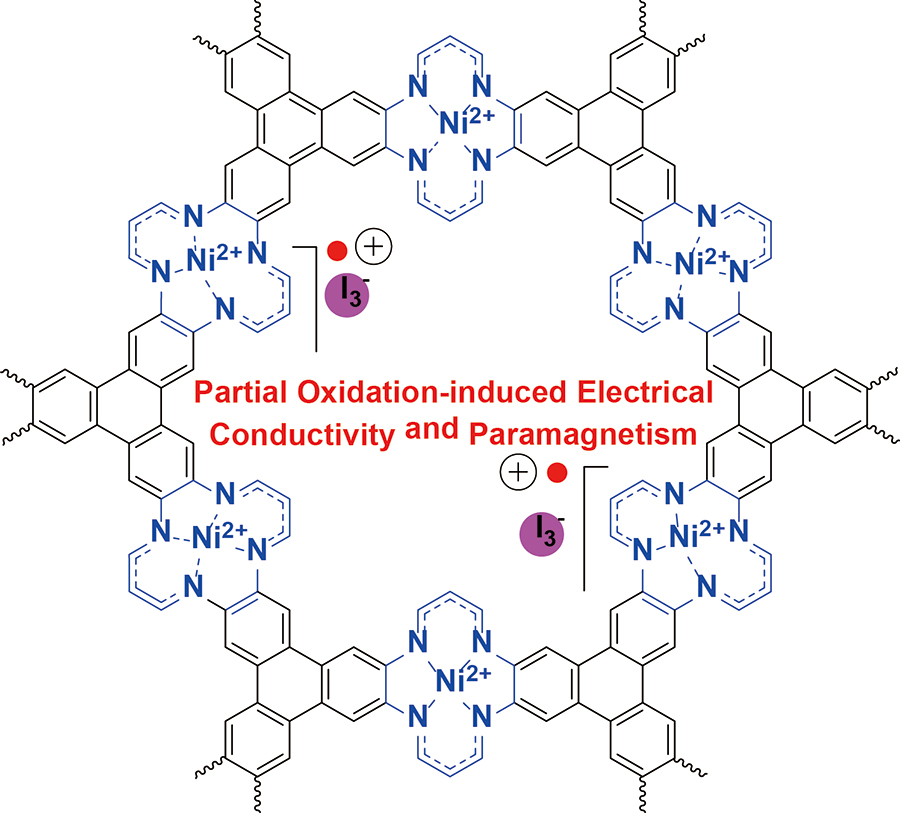
IBS 다차원 탄소재료 연구단은 요오드 도핑에 의한 부분적 산화를 통해 전기전도성 및 상자성을 갖는 NiTAA-MOF를 개발했다.
▲ 그림 3. 요오드 도핑된 NiTAA-MOF 펠렛
직경 약 1.5cm의 요오도 도핑된 NiTAA-MOF 펠렛(디스크 형태)의 모습
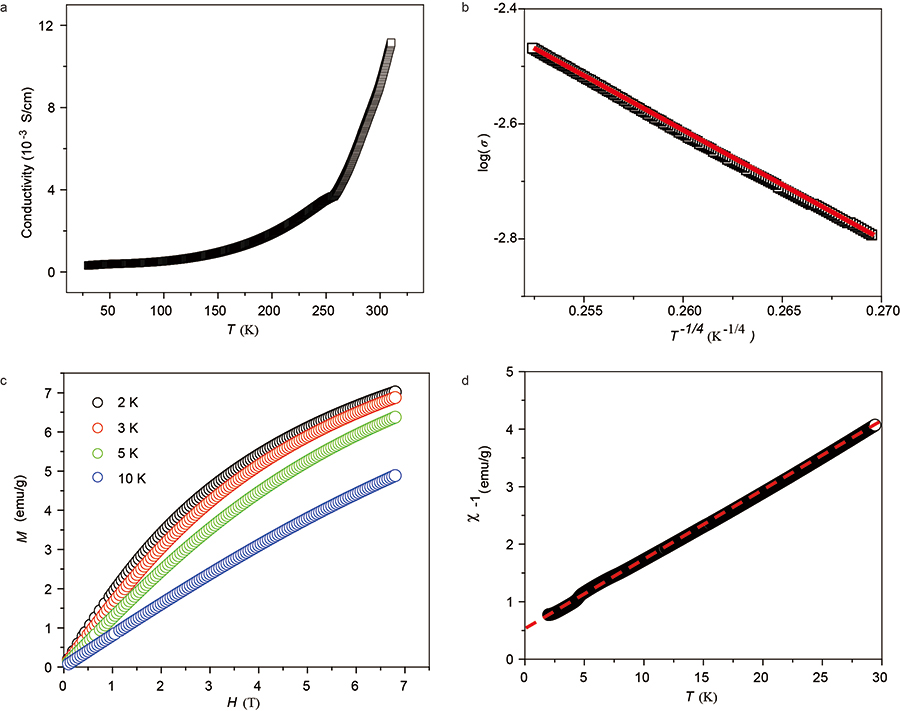
▲ 그림 4. 요오드 도핑된 NiTAA-MOF의 전기전도성 및 자성 특성
(c)다양한 온도에서 측정된 NiTAA-MOF의 자기장 의존 자기 곡선. (d) 반강자성 상호작용을 보여주는 자화의 온도 의존성.
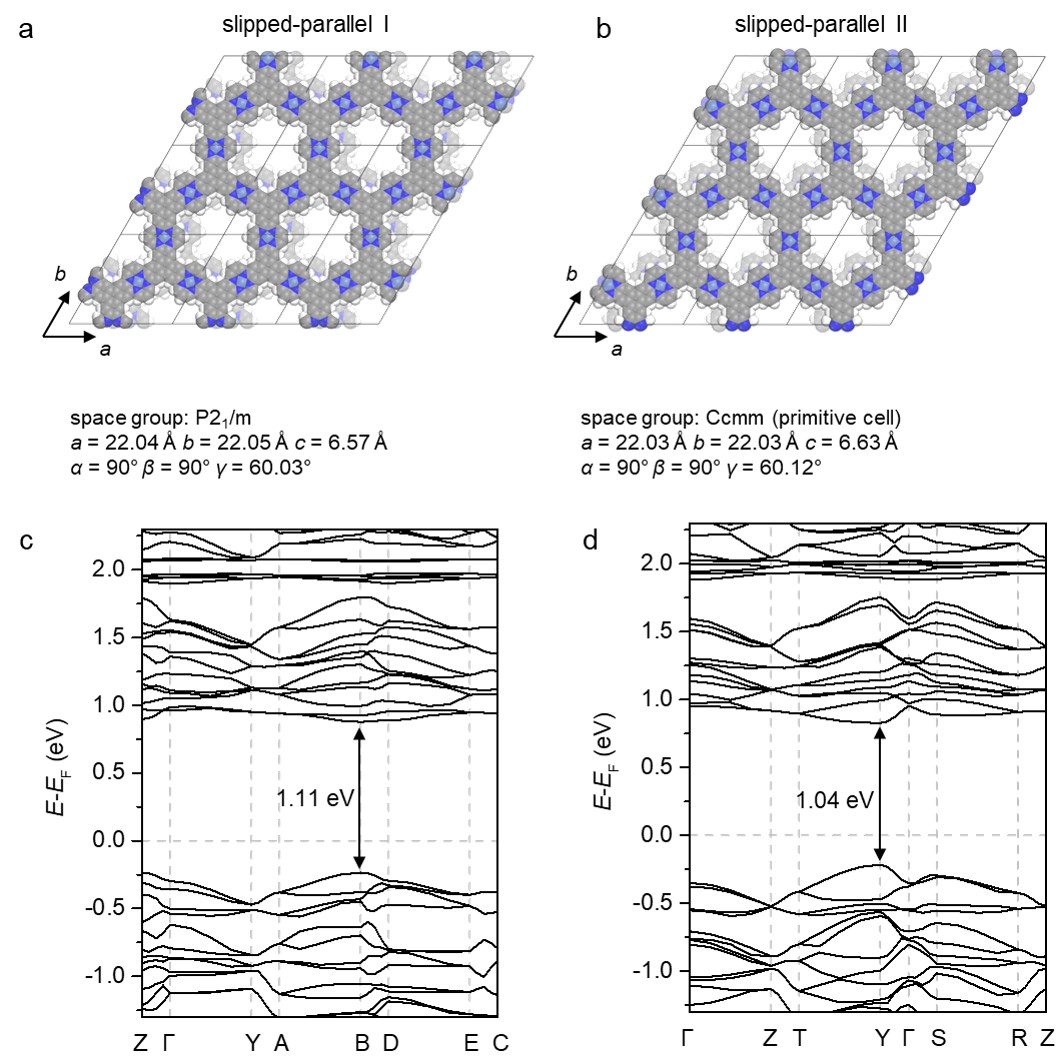
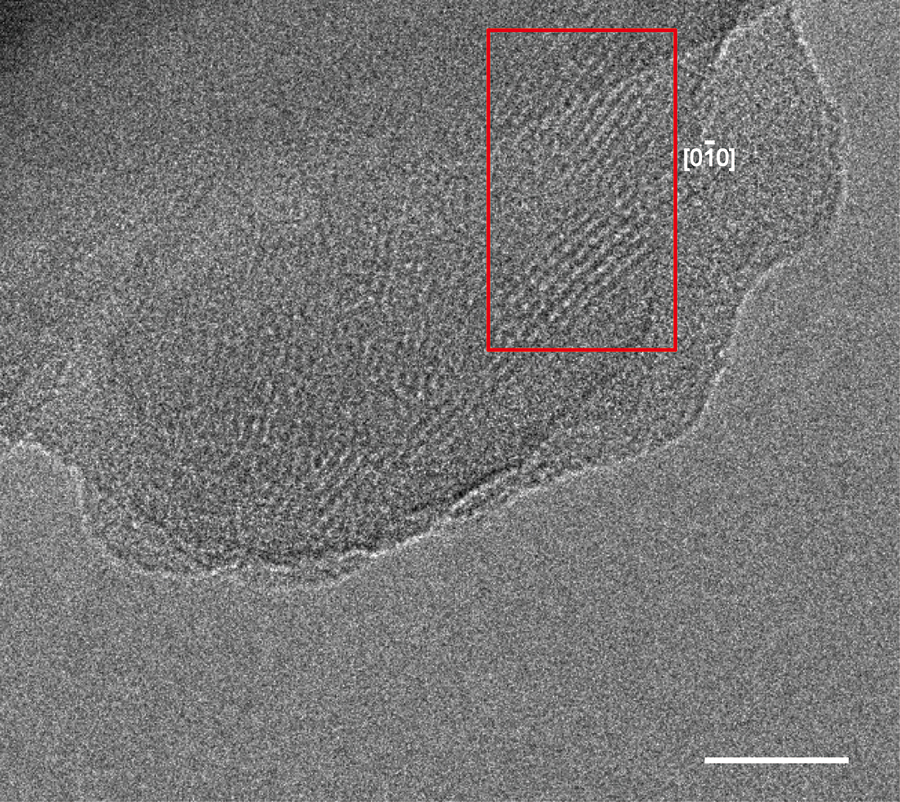
▲ 그림 5. NiTAA-MOF의 적층 구조 및 전자 밴드 구조
합성한 NiTAA-MOF를 고분해능 투과전자현미경으로 촬영한 모습. 우측 하단의 흰 막대는 20nm를 나타낸다.
