UPDATES
Peeling Graphene from Copper
- Elucidating the intercalation mechanism and pathways for graphene decoupling from the copper substrate -
August 30, 2016
A recent quantum chemistry study related to delamination of graphene from Cu foil substrates by a research team at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) has provided important information about the intercalation mechanism and pathways for graphene decoupling from the copper substrate through the formation of copper oxide, which has a weaker binding to the graphene than the pure Cu does.
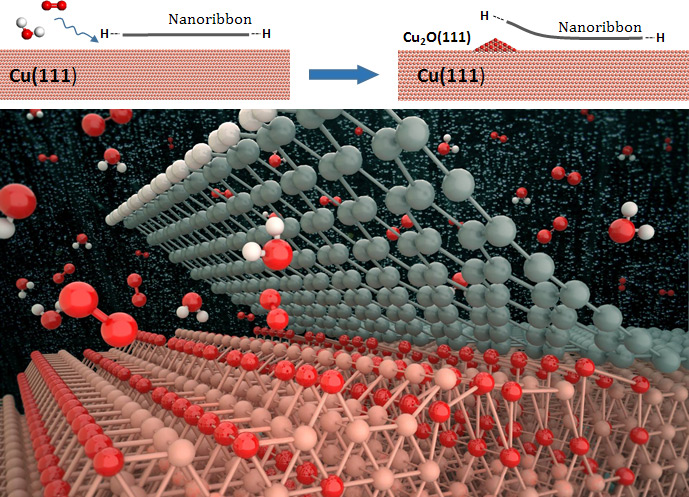
The graphene films, grown on the copper (Cu) substrates must be detached clean without leaving residue behind, as residual metallic impurities can significantly alter electronic and electrochemical properties of graphene. However, thanks to recent advances in graphene transfer method, the electrochemical corrosion of graphene coatings on Cu has allowed the monolayer-thick material to be mechanically delaminated without significantly compromising its structural integrity.
The new UNIST graphene research veers off in a new direction by succesfully separating graphene from its metal growth substrates without the assistance of the adhesive tape. The research findings have been published in the August issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
In the study, led by Prof. Sang Kyu Kwak (School of Energy and Chemical Engineering) and Prof. Rodney Ruoff (Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials), the research team revealed the surface oxidation chemistry of the nanoribbon-covered Cu(111) surface.
Specifically, they have demonstrated that the graphene nanoribbon (GNR) edge type influences the initial oxidation stages of the Cu surface, thus driving the nanoribbon decoupling by the intercalation of surrounding adsorbate molecules (e.g. oxygen and water).
The difference between the armchair GNR and zigzag GNR on the Cu(111) substrate, is distinguished by the presence of an edge state in the zigzag GNR edges, which has been attributed to the hybridization between the out-of-plane carbon π orbitals and the metal d orbitals. This edge state, however, is absent in the armchair GNR edge atoms. Such an observation has not been reported for H-terminated GNR on Cu(111).
Vibrational stretching mode calculations showed that the GNR edges influenced the molecular adsorption of oxygen at the bare and GNR/Cu sites, confirming the role of GNR edges in weakening the pre-elongated O-O bond at the GNR/Cu interface. The research team also explained that the GNR edges facilitated the stabilization of water molecules (regardless of surface oxygenation), which would otherwise be unstable on the bare Cu surface.

Dr. Kester Wong, who takes full charge of the research, notes that "GNR-mediated interactions between water and the chemisorbed oxygen radicals can shed further light in elucidating the role of water and oxygen in the surface oxide formation."
"This particular study may have interesting implications for the development of regioselective graphene-based catalysis. Nonetheless, employing other crystal facets for the interfacial study of low dimensional materials is of great interest, and several investigations are being heavily pursued by our group in this area", says Prof. Kwak.
This work has been supported by Institute of Basic Sciences (IBS, CMCM) and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Korean Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (MSIP).
Joo Hyeon Heo (UNIST, Public Relations Team)
Notes for editors
- References
Kester Wong, Seok Ju Kang, Christopher W. Bielawski, Rodney S. Ruoff, and Sang Kyu Kwak, "First-Principles Study of the Role of O2 and H2O in the Decoupling of Graphene on Cu(111)", Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138 (34), 10986–10994. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b05333
- Media Contact
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact: Ms Joo Hyeon Heo, UNIST Public Relations Team (+82-52-217–1223, joohyeonheo@unist.ac.kr)
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea It comprises a total of 50 research centers in all fields of basic science, including mathematics, physics, chemistry, life science, earth science and interdisciplinary science. IBS has launched 26 research centers as of September 2016. There are eight physics, one mathematics, six chemistry, eight life science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
